
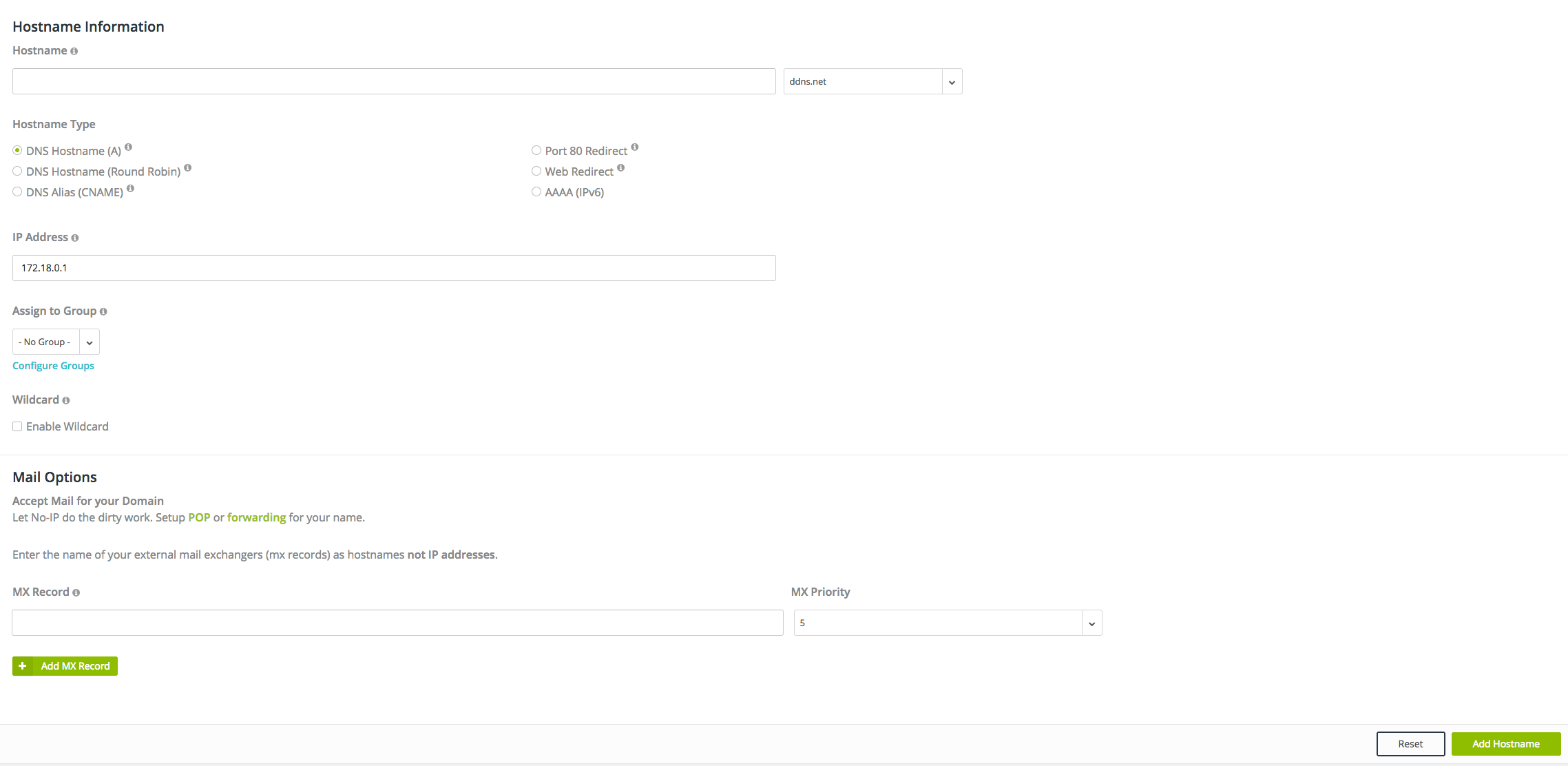
SET SERVER IP SIMPLE DNS PLUS CODE
The source code is not centrally maintained and was released into the public domain in 2007. In March 2009, Bernstein paid $1000 to the first person finding a security hole in djbdns. Bernstein, author of qmail, with an emphasis on security considerations.
SET SERVER IP SIMPLE DNS PLUS SOFTWARE
Its goal is to route traffic to the best server, delivering better performance to legitimate users while shunting or blocking abusive traffic.ĭjbdns is a collection of DNS applications, including tinydns, which was the second most used free software DNS server in 2004. It loads the contents of /etc/hosts, so that local host names which do not appear in the global DNS can be resolved.ĭnsdist is a DNS-, DoS- and abuse-aware load balancer. It can serve the names of local machines which are not in the global DNS.ĭnsmasq accepts DNS queries and either answers them from a small, local cache or forwards them to a real, recursive DNS server. Dnsmasq ĭnsmasq is a lightweight, easy to configure DNS forwarder, designed to provide DNS (and optionally DHCP and TFTP) services to a small-scale network. It supports high rates of dynamic update.ĬoreDNS is the recommended DNS server for Kubernetes and graduated from the CNCF in 2019. The BIND 10 codebase continues on as an open source project at ( ibid.) It is not included in this comparison at this time.ĬNR includes a commercial DNS server from Cisco Systems usually used in conjunction with the CNR DHCP ( Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server. ISC cited a lack of resources to continue development of BIND 10, and they reaffirmed their commitment to BIND9. Its first release was in April 2010, but ISC involvement concluded with the release of BIND 10 version 1.2 in April 2014. Internet Systems Consortium started development of a new version, BIND 10. BIND9 is a ground-up rewrite of BIND featuring complete DNSSEC support in addition to other features and enhancements. BIND4 and BIND8 are now technically obsolete and not considered in this article.

Historically, BIND underwent three major revisions, each with significantly different architectures: BIND4, BIND8, and BIND9. It is the most widely deployed DNS server. It is a free software product and is distributed with most Unix and Linux platforms, where it is most often also referred to as named (name daemon). Key advantage is to use the same application delivery controller to support DNS and application acceleration.īIND is the de facto standard DNS server. Most Internet users access a recursive server provided by their internet service provider to locate internet hosts such as BIG-IP DNS į5 Networks product offers DNS as an authoritative server, recursive and adds additional security measures.
They also (typically) cache the result to answer potential future queries within a certain expiration ( time-to-live) period.

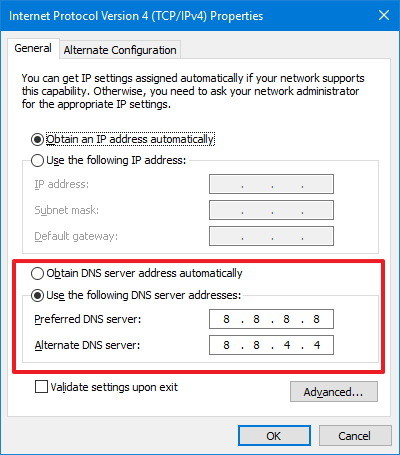


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
